
Start with Basics of Python – Part 1
Dot Notation
Using dot notation with strings.
Let us consider an example where we convert the string to upper case using dot notation.
>>> mysore = “The city is awesome !”
>>> print len(mysore)
>>> print mysore.upper()
Printing strings
>>> print(“This String”)
Printing Variables
>>> Stone_cold = “Stunner”
>>> print(Stone_cold)
Concatenation
Combining strings together is called concatenation . The + operator combine the strings.
>>> print “Indian “+ “Air ” +”Force ”
The space after the word is to make the string look like sentence.
String Conversion
The str() method converts non-strings into strings.
>>> print “Sourav Ganguly scored “+ str(100) + “on his Test Debut”
String Formatting
The % operator after a string combines a string with variables. The % operator will replace %s in the string with the string variable.
Example 1:
>>> string_1 = “Sourav”
>>> string_2 = “Dada”
>>> print “Indian captain %s is also called as %s.” % (string_1, string_2)
Example 2:
>>> batsman = raw_input(“Who is the batsman?”)
>>> captain = raw_input(“Who is the captain?”)
>>> series = raw_input(“Which series did he win for India?”)
>>> print “The Indian %s and %s Sourav Ganguly won %s series for India.” % (batsman, captain, series)
Date and Time
We can import datetime function from datetime module.
>>> from datetime import datetime
Current Date and Time
Here is the code to print current date and time.
>>> from datetime import datetime
>>> now = datetime.now()
>>> print datetime.now()
Control Flow
The ability to choose from different situations based on what’s happening in the program.
>>> x = int(input(“Please enter an integer: “))
Please enter an integer: 35
>>> if x < 0:
… x = 0
… print(‘Negative changed to zero’)
… elif x == 0:
… print(‘Zero’)
… elif x == 1:
… print(‘Single’)
… else:
… print(‘More’)
if statements, for statements, range fuction, break and continue, else clause loops, pass statements are few of the control flow statements.
Comparators
Equal to (==)
Not equal to (!=)
Less than (<)
Less than or equal to (<=)
Greater than (>)
Greater than or equal to (>=)
Boolean Operators
AND
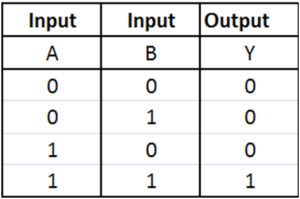
OR 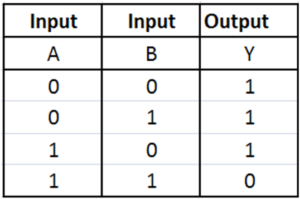
NOT
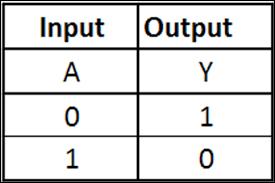
Conditional Syntax
The statements used for decision making are called conditional statements.
if condition_1:
statement_block_1
elif condition_2:
statement_block_2
else:
statement_block_3
This post concludes basics of python.

Facebook Comments