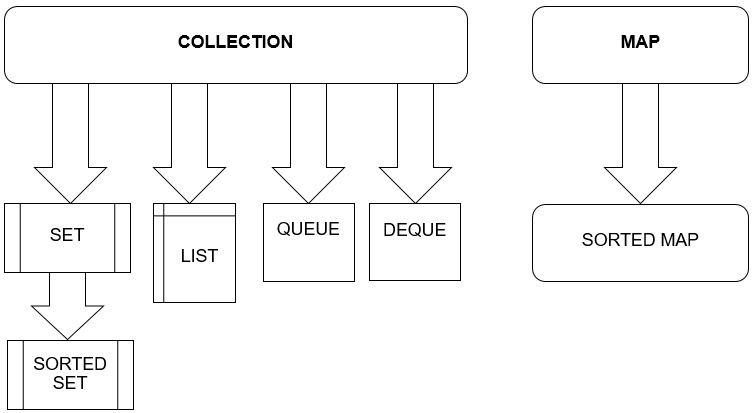
Most algorithms in Java operate on list instances and subsequently with other collection instances. The different algorithms used in Java are:
- Sorting
- Shuffling
- Routine Data Manipulation
- Searching
- Composition
- Finding Extreme Values
Sorting
The sort algorithm reorders a List so that its elements are in ascending order according to an ordering relationship. Two forms of the operation are provided.
FORM 1
The simple form takes a List and sorts it according to its elements’ natural ordering.
The sort operation uses a optimized merge sort algorithm which is fast and stable:
- Fast: It is guaranteed to run in n log(n) time and runs substantially faster on nearly sorted lists. Empirical tests showed it to be as fast as a highly optimized quicksort. A quicksort is generally considered to be faster than a merge sort but isn’t stable and doesn’t guarantee n log(n) performance.
- Stable: It doesn’t reorder equal elements. This is important if you sort the same list repeatedly on different attributes. If a user of a mail program sorts the inbox by mailing date and then sorts it by sender, the user naturally expects that the now-sequential list of messages from a given sender will (still) be sorted by mailing date. This is guaranteed only if the second sort was stable.
FORM 2
The second form of sort takes a Comparator in addition to a List and sorts the elements with the Comparator.
Shuffling
The shuffle algorithm does the opposite of what sort does, destroying any trace of order that may have been present in a List. That is, this algorithm reorders the List based on input from a source of randomness such that all possible permutations occur with equal likelihood, assuming a fair source of randomness. This algorithm is useful in implementing games of chance.
This operation has two forms:
One takes a List and uses a default source of randomness, and the other requires the caller to provide a Random object to use as a source of randomness.
Routine Data Manipulation
The Collections class provides five algorithms for doing routine data manipulation on List objects, as listed below:
- reverse — reverses the order of the elements in a List.
- fill — overwrites every element in a List with the specified value. This operation is useful for reinitializing a List.
- copy — takes two arguments, a destination List and a source List, and copies the elements of the source into the destination, overwriting its contents. The destination List must be at least as long as the source. If it is longer, the remaining elements in the destination List are unaffected.
- swap — swaps the elements at the specified positions in a List.
- addAll — adds all the specified elements to a Collection. The elements to be added may be specified individually or as an array.
Searching
The binarySearch algorithm searches for a specified element in a sorted List. This algorithm has two forms.
- The first takes a List and an element to search for (the “search key”). This form assumes that the List is sorted in ascending order according to the natural ordering of its elements.
- The second form takes a Comparator in addition to the List and the search key, and assumes that the List is sorted into ascending order according to the specified Comparator. The sort algorithm can be used to sort the List prior to calling binarySearch.
The return value is the same for both forms.
Composition
The frequency and disjoint algorithms test some aspect of the composition of one or more Collections:
- frequency — counts the number of times the specified element occurs in the specified collection.
- disjoint — determines whether two Collections are disjoint; that is, whether they contain no elements in common.
Finding Extreme Values
The min and the max algorithms return, respectively, the minimum and maximum element contained in a specified Collection. Both of these operations come in two forms.
The simple form takes only a Collection and returns the minimum (or maximum) element according to the elements’ natural ordering.
The second form takes a Comparator in addition to the Collection and returns the minimum (or maximum) element according to the specified Comparator.
Source: The Java™ Tutorials