A positive attitude usually results in a favorable outcome. You have nothing to loose by being positive.
Law of Action : Economics and Startups
Newton’s 3rd law states :-
“For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.”
A simple action such as walking proves the validity of the above statement, when we push our feet backwards on the ground, our body moves forward.
Does this mean all actions are bound to this law ?
Yes, if not all actions, most of them are bound to this law.
A ball pushed downwards on water surface bounces back due to the buoyancy exhibited by water.
A ball thrown up must come back because of gravity.
This law holds good even in the world of Economics and Startups, wonder how ?
Trade markets, Financial results, traction all these are driven by a law of action.
Cause and effect is a normalizing feature associated in Economics.
But is the world ready for a level playing field ?
No it isn’t and it will never be.
Every product created which exists is bound by this law of action.
Action and Reaction constitute a single entity. A pure play source of energy being transferred between two states.
A Startup in order to succeed must have necessary traction, if traction is the result, there needs to be a action in-order to achieve the desired result.
A chain of individual components and the synergy generated by this chain is what makes a startup succeed.
Everything that matters must be active in order to succeed. Being active at the right moment results in stupendous success.
To get the timing right is one thing and to get the time going with a thing is another. The former is the action and the latter is its reaction.
Mysuru Dasara : State Festival of Karnataka
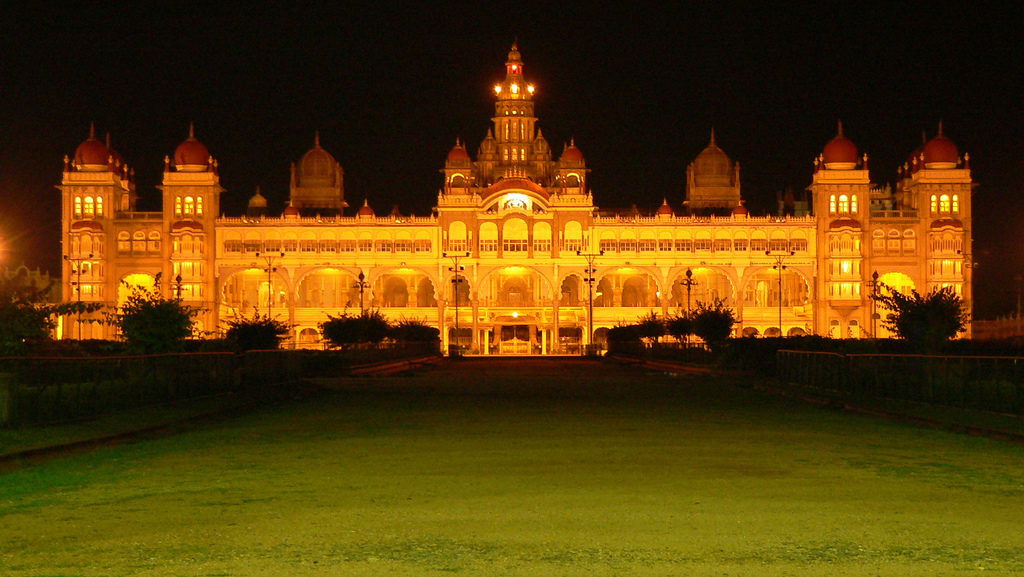

The legacy of Mysuru Dasara festival dates back to four centuries ago. The 10 days of celebration in Mysuru city represents the tradition and rich cultural heritage of Karnataka. During these 10 days Mysuru city and Mysuru palace is decorated and grandeur of the place is reclaimed.
The story of Mysuru getting it’s name gives a picture of the place and festival.
Mysuru gets it’s name from a asura(demon) known as Mahishasura.
Folktales of this place or the history here says that long ago in Mysuru lived Mahishasura who performed deep penance and requested a boon from lord Brahma.
The boon was that ‘Mahishasura should not have death’. Brahma to which replied all beings that are born must die. In turn Mahishasura asked for a boon that if he must die, let it be at the hands of a woman. To which Brahma agreed and granted the boon.
When Mahishasura became invincible, goddess Chamundi(a form of goddess Durga) was born in order to kill Mahishasura. A fierce battle ensued between Mahishasura and Chamundi before Mahishasura was killed.
Hence, the name Mysuru for the place.
Untill 1973, the present state of Karnataka was known as Mysore state.
Chamundi hills located close to the city of mysuru is the abode of goddess Chamundi.

The state goddess Chamundi is carried on a procession by a group of elephants with Arjuna(chief elephant 2018) carrying 750 Kg golden howdah having the idol of goddess chamundi.
People from various countries and states arrive at Mysuru to experience the beauty of this occasion.
On this auspicious day, wishing everyone a happy Dasara.
Quote for the day – 28th September 2018
Application of skills and being resourceful is a tribute to accumulated knowledge.
Happy Independence Day 2018 India

To the land of my birth, to my home, to the mother of a billion and more, I wish a happy independence day. To my fellow Indians, wishing you all a happy independence day 2018.
Quote for the day – 7th August 2018
Give me a good product with excellent service – you can count me as a consumer of that product forever.
Quote for the day – 11th July 2018
Art and science are like heart and mind; one complementing the other.
Happy Independence Day 2018 United States of America

To the land of opportunities and entrepreneurs, wishing a happy independence day 2018. Love from India.
Quote for the day – 29th June 2018
Blockchain will be banked upon by banks.
Quote for the day – 26th June 2018
The older I get, greater is my respect towards my parents, to hold them in high regards.
